Cell culture aspiration is a critical technique that holds significant importance in biological research and medical laboratories. Understanding and discussing this topic is essential due to its wide-ranging applications and contributions to various fields. Cell culture aspiration enables researchers to isolate specific cell populations, collect desired cellular components, and remove unwanted contaminants from cultures.
This technique plays a crucial role in cell line maintenance, drug development, tissue engineering, and the study of cellular behavior. By exploring the intricacies of cell culture aspiration, scientists can enhance experimental precision, improve cell-based assays, and advance our understanding of fundamental biological processes.
Therefore, delving into the topic of cell culture aspiration is crucial for researchers seeking to achieve accurate and reliable results in their scientific endeavors.
What is cell culture aspiration?
Basic cell culture procedure
Comparison of lab aspiration systems
Aspiration system and cell culture lab essential
Handling and disposal of liquid waste
What is cell culture aspiration?
Aspiration or suction is a commonly used technique in modern biological technology, such as cell culture, for the removal of liquid media. Cell culture refers to the process of culturing eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells in a controlled environment, allowing them to grow and proliferate in a culture medium. In the laboratory, aspiration is frequently employed to remove the culture medium metabolized by the cells using a vacuum generated by an aspiration pump.
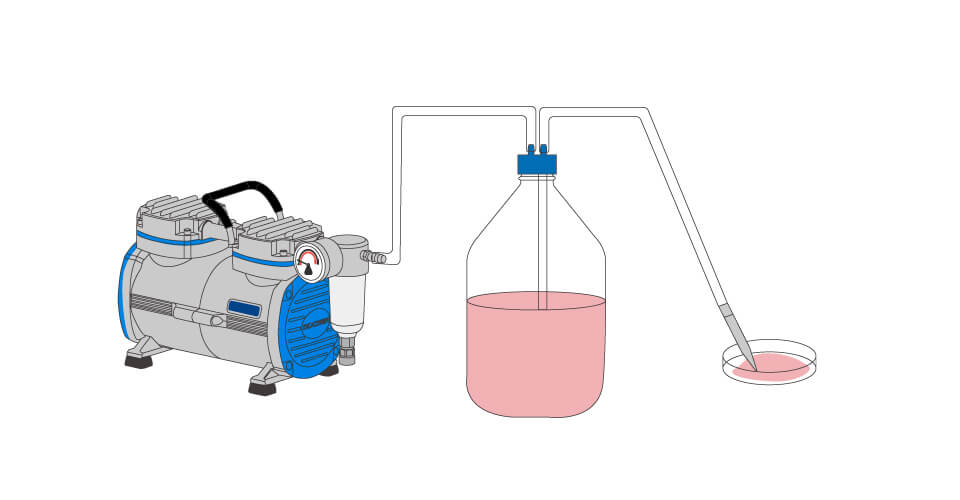
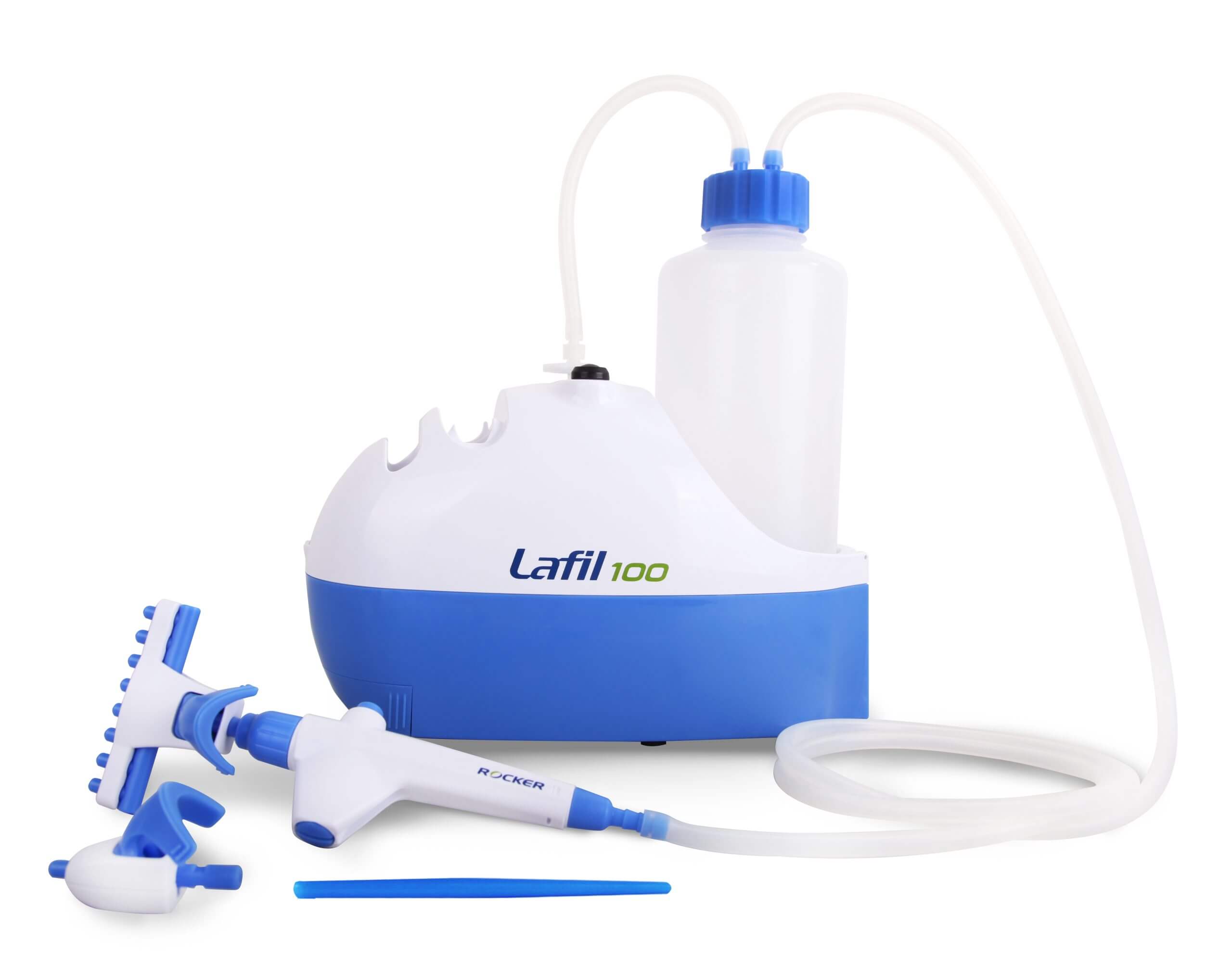
A vacuum aspiration system commonly used in cell culture labs typically consists of the following components:
-
- Vacuum flask: This container is used to collect the aspirated liquid.
- Safety bottle: Its purpose is to prevent the liquid from being drawn into the vacuum source or vacuum pump.
- Filter: A HEPA (High Efficiency Particulate Air) filter or a 0.22µm filter is employed to prevent particles and maintain optimal suction efficiency.
- Vacuum source / aspiration pump: This device creates the necessary vacuum or negative pressure to aspirate the liquid when the pipes are connected.
When the pipes are connected to the vacuum source, the pressure difference causes the liquid to be aspirated into the vacuum flask. The safety bottle acts as a protective barrier to prevent the liquid from entering the vacuum source or vacuum pump. Filters, such as HEPA filters or 0.22µm filters, are used to prevent particles from interfering with the suction efficiency.
Basic Cell Culture Procedure
- Thawing cells: Thaw frozen cells rapidly in a 37°C water bath for approximately 1 minute to prevent cell damage.
- Cell culture: Depending on the type and concentration of the cells, thoroughly mix them with the culture medium and allow them to rest in an incubator for cultivation.
- Cell subculture: Passaging involves diluting cells that have reached high confluence with fresh medium to support their continuous propagation in culture.
It is not advisable to passage cells at the stationary phase because they tend to take longer to enter the logarithmic growth phase after seeding. Furthermore, the accumulation of lactic acid in dense cultures can impact cell metabolism.
a. Adherent cell, or so-called monolayer culture
- Remove the medium from the dish.
- Wash the cells with a calcium- and magnesium-free balanced salt solution, such as phosphate-buffered saline or Hanks’ balanced salt solution.
- Add a detaching agent, such as trypsin, and incubate at 37°C until the cells are fully detached from the dish. The incubation time can range from 2 to 20 minutes, depending on the cell line.
- Resuspend the cells in fresh medium and pipette thoroughly to obtain a single-cell suspension. If your medium does not contain serum, it is necessary to inactivate the detaching agent, for example, by adding trypsin inhibitors.
- Measure the total number of cells by performing cell counting techniques.
- Plate the cells onto a new dish at the desired cell density.
b. Suspension cell, or so-called suspension culture
- Collect cells along with the medium and perform a brief centrifugation at 150–300 xg for 3–5 minutes to pellet the cells.
- Remove the medium and gently resuspend the cells using a balanced salt solution. Perform another brief centrifugation at 150–300 xg for 3–5 minutes to pellet the cells.
- Remove the salt solution and resuspend the cells in fresh medium. Measure the total number of cells using appropriate cell counting methods.
- Plate the cells onto a new dish at the desired cell density.
- Cryopreservation: Resuspend cells in medium with 5% to 10% DMSO (Dimethyl sulfoxide) and 30% to 50% FBS (Fetal Bovine Serum) and freeze at -80 °C
- Cell counting: Count cells with a Neubauer chamber or other auto counters then calculate cell concentration.
Comparison of lab aspiration systems
There are various methods for liquid aspiration or suction in laboratories. In the past, pipettes were commonly used for liquid removal. However, this method could lead to muscle soreness or even injury due to the repetitive press-and-release movement. Additionally, it often required a large number of disposable pipette tips, which raised environmental concerns.
In contrast, modern laboratories tend to favor self-installed vacuum aspirators. These systems are more efficient than traditional pipetting methods. However, poor piping layout and the use of fragile glass flasks and pipes can pose potential safety risks in the lab.
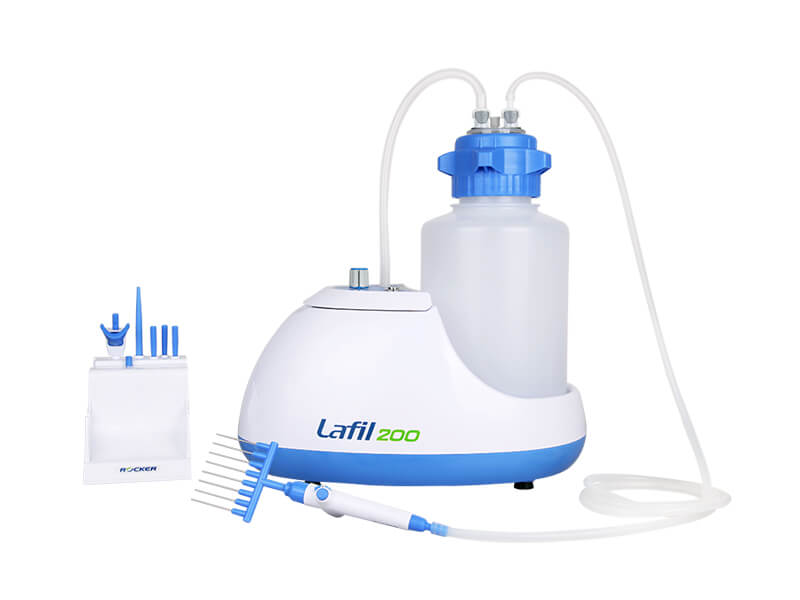
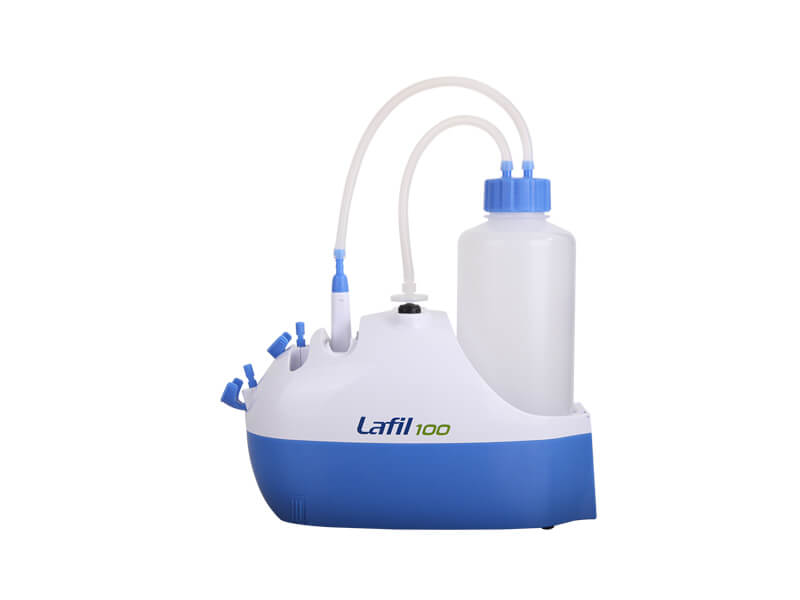
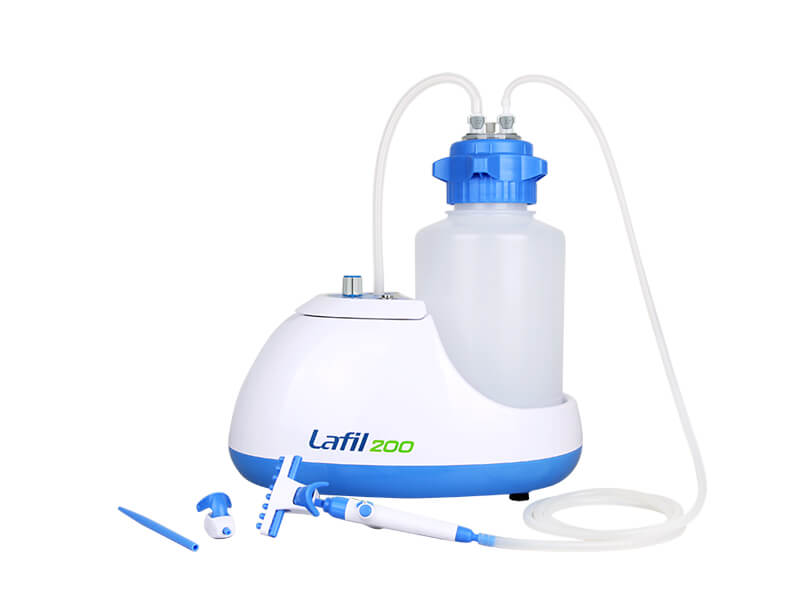
The Rocker Lafil series suction system is a unique integrated bio-suction system that combines a vacuum source with a suction kit. Its compact design saves more bench space compared to other traditional systems. The system features a fence-like platform design that helps prevent accidental tipping of the suction bottles, ensuring user safety.
Rocker Lafil Suction System and BioDolphin Suction Kit
Lafil Suction Systems
|
|
Lab Pipette |
Self-installed Vacuum Aspirator |
ROCKER Lafil Bio-suction System |
|
|
Integrated |
Yes. It’s a single product. |
No |
Yes, all-in-one design |
|
|
Consumables |
Disposable serological pipettes |
tips |
tips |
|
|
Long operation |
Muscle soreness |
Muscle soreness |
Ergonomic design with easy tip-ejector |
|
|
Suction adjustment |
None |
Yes |
None |
Yes |
|
Liquid exhaust |
Each time of pipetting |
Until fullness of bottle |
Until fullness of bottle |
|
|
Vacuum bottle |
None |
1 L PP bottle |
1 L PP bottle or glass bottle |
4 L PP bottle or glass bottle |
|
Protection |
None |
None |
Yes |
|
|
Risk to spill |
None |
High |
None |
|
|
In-hood operation |
Possible |
Not possible |
Possible |
Not possible |
|
Space-taking |
Small |
Large |
50~65% space of self-installed systems |
|
|
Environmental concerns |
Large amount of disposable plastics. |
Large amount of disposable plastics. |
Reusable, autoclavable tools. |
|
|
Other |
|
|
Lafil 200 model supports two aspiration tools at once. |
|
Aspiration system and cell culture lab essential
|
Cell Culture Hood (i.e., laminar-flow hood or biosafety cabinet) |
The cell culture hood provides an aseptic work area, ensuring a sterile environment for performing microbiological procedures. It also serves as a containment system, effectively preventing the spread of infectious splashes or aerosols that may be generated during these procedures. |
|
Incubator |
The purpose of an incubator is to provide the optimal environment for cell growth. It achieves this by precisely controlling the temperature, humidity level, and CO2 concentration. By maintaining these parameters at the desired levels, incubators create conditions that promote the healthy growth and proliferation of cells. |
|
Aspiration System |
A pump, also known as an aspiration system, is utilized in the laminar flow hood to facilitate the easy removal of media and reagents from cell culture vessels. This equipment enables efficient and controlled aspiration, allowing for the convenient transfer or removal of liquids during cell culture procedures. |
|
Optical Microscope |
An optical microscope, including both upright and inverted microscopes, is an indispensable tool in a cell culture laboratory. It plays a crucial role in visualizing cells for various purposes such as monitoring cell morphology, cell counting, and identifying potential contamination. These microscopes enable researchers to observe cells directly, providing valuable information for assessing cell health and ensuring the quality of cell cultures. |
|
Cryogenic Storage (i.e., ultra-low freezer) |
Cell lines in continuous culture are susceptible to genetic instability, including genetic drift and senescence, as they undergo repeated passages. To mitigate this issue, it is crucial to prepare working stocks of the cells and preserve them through cryogenic storage for long-term storage. By freezing cells at low temperatures using cryoprotective agents, such as dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), the viability and genetic integrity of the cell line can be maintained, ensuring a stable and reliable cell source for future experiments. |
|
Water Bath |
A water bath set to 37°C is a common equipment found in cell culture laboratories. It serves multiple purposes, including pre-warming the cell culture medium prior to use and thawing frozen cells and reagents. By maintaining a constant temperature of 37°C, the water bath provides a controlled and gentle heating environment that ensures the proper temperature for these critical cell culture procedures. This helps to maintain the viability and functionality of cells and reagents during thawing and preparation. |
Handling and disposal of liquid waste
Organic liquid waste containing hazardous chemicals, such as chlorine, must be collected in suitable containers and labeled properly to ensure safe handling and disposal.
Non-hazardous chemical liquids can be collected in general waste containers designated for liquids or oils.
Liquids like cell culture medium or supernatants should be treated with an appropriate concentration of disinfectants, such as bleach (sodium hypochlorite), to effectively inactivate the cells before being disposed of down the drain.
Other biomedical waste, including petri dishes and other consumable materials, should be placed in biomedical waste bags and sterilized using an autoclave prior to disposal. It is important to adhere to local regulations and guidelines regarding the proper disposal of biomedical waste.
References:
1) Cell Culture Basics: Equipment, Fundamentals and Protocols | Technology Networks
2) CellCultureBasicsEU.pdf (vanderbilt.edu)
3) Environmental Protection Administration, Executive Yuan, R.O.C.(Taiwan) -Chinese Content (epa.gov.tw)