Wastewater definition & indicators
COD Test (Chemical Oxygen Demand)
Determination of Total Ammonia Nitrogen (TAN)
Determination of Total Phosphorus (TP)
Determination of Total Nitrogen (TN)
Wastewater definition & indicators
Wastewater is used water that has been affected by domestic, industrial and commercial use. The composition of wastewater normally is 99.9% water and the remaining 0.1% is what is removed. This 0.1% may contain organic matter, microorganisms and inorganic compounds. Wastewater effluents are released to a variety of environments, such as lakes, ponds, streams, rivers, estuaries and oceans. Wastewater also includes storm runoff, as harmful substances wash off roads, parking lots and rooftops.
There are physical, chemical and biological indicators that may affect wastewater quality, includes temperature, total suspended solids (TSS), pH value, oxygen and oxygen demand, nitrogen, phosphorus, chlorine and micro-organisms. In this assay, we’ll discuss more about the chemical indicators of wastewater quality including oxygen demand, total ammonia nitrogen, total phosphate and total nitrogen.
Read more about:
Total Suspended Solids Test
Microbiological Test
Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) Test
Chemical oxygen demand (COD) is a method to determine the quantity of pollution in water. The higher value of chemical oxygen demand indicates the higher organic pollution in the water sample. As compared to Biological Oxygen demand test, COD takes less time to process, thus is recommended where the water has toxicity and organic matter that cannot be determined by biological oxygen demand.
Steps of COD Tests
- Select the appropriate concentration of reagent vial according to the COD concentration of sample.
- Add 2 mL pure water to one COD reagent vial as the blank sample.
- Add 2 mL test sample to another COD reagent vial as the test sample.
- Tighten the cap and shake slightly to mix evenly.
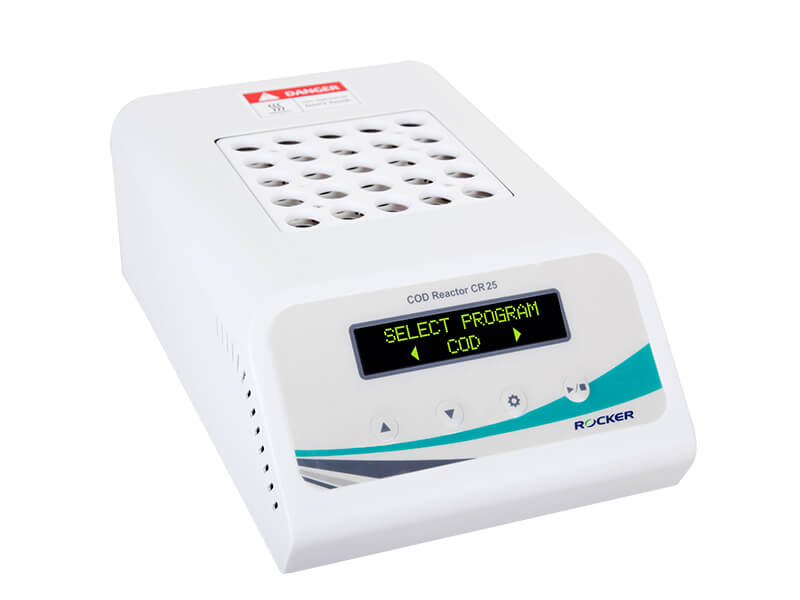
- Put the vials into the COD reactor (CR 25), start COD program for 150 oC, 2 hours.
- Remove the vials and cool them down to room temperature.
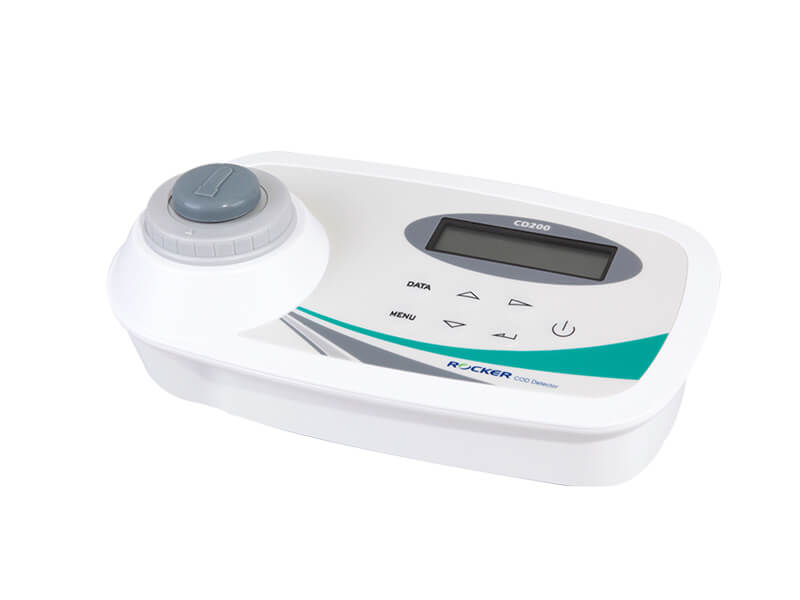
- Turn on the COD detector (CD 200) and insert the blank sample vial into it to start a zero calibration.
- Insert the test sample vial into the COD detector (CD 200) to get the COD concentration of the sample.
Determination of Total Ammonia Nitrogen (TAN)
What is total nitrogen in wastewater?
Ammonia nitrogen is a form of nitrogen consists of non-ionized ammonia (NH3) and ammonium ion (NH4 +) and is a major pollutant in wastewater. Ammonia molecules (ammonia, NH3) and ammonium ions (ammonium, NH4+) in water are converted to each other under different pH and temperature conditions.
Harm of ammonia nitrogen in water
In the nitrogen cycle with sufficient oxygen, ammonia nitrogen can be converted into nitrite and nitrate, which may cause cancer in human body. Dissolved ammonia can also be toxic to fish, and discharge of ammonia nitrogen into the water may promote eutrophication thus reduce amount of dissolved oxygen. Either case may result in fish deaths.
Determination of ammonia nitrogen – Salicylate method
In Salicylate method, Ammonia compounds are initially combined with hypochlorite to form monochloramine (1), which then reacts with salicylate to form 5-aminosalicylate (2).
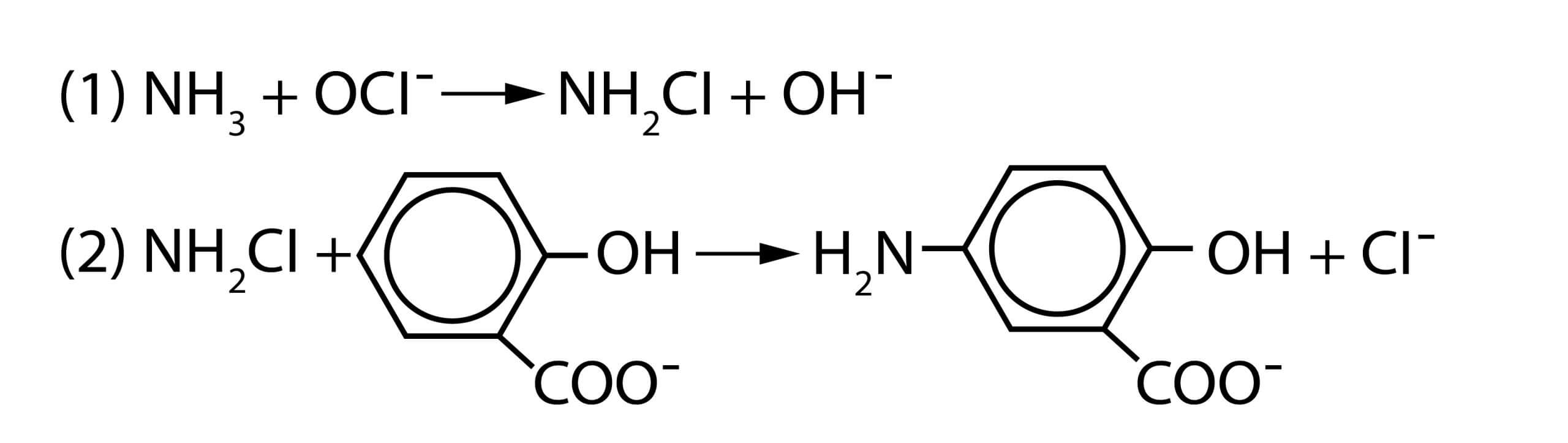
Oxidation of 5-aminosalicylate is carried out in the presence of a catalyst, nitroprusside or Fe(CN)5NO2– (also called nitroferricyanide), which results in the formation of indosalicylate, a blue-colored compound. The blue color is masked by the yellow color (from excess nitroprusside) causing a green-colored solution. The intensity of the color is directly proportional to the ammonia concentration in the sample.
ROCKER’s COD-test-related products include a reactor, the CR 25, and readers. Compliant with USEPA 410, the CR 25 COD reactor performs closed micro reflux method for metal digestion. The readers, CD 200 and WD 200 are easy to use with their pre-defined programs for COD, Total Phosphorus, Total Nitrogen and Ammonia Nitrogen values.
ROCKER’s Water Analysis Products
Mars Graphite Heat Plate
Determination of Total Phosphorus (TP)
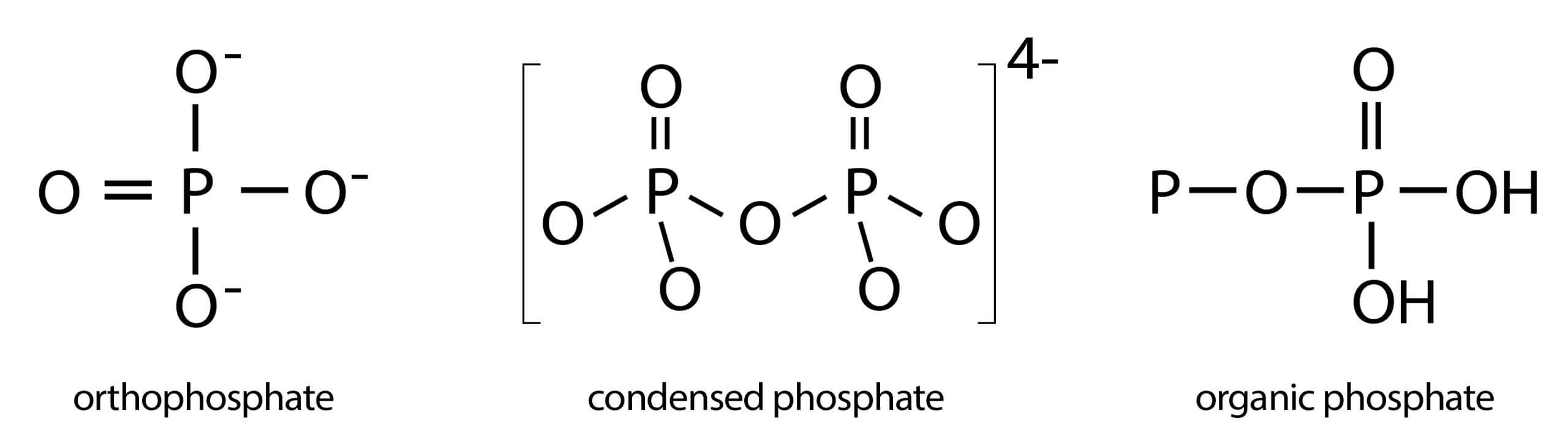
What is Total Phosphate
Total phosphate is composed of orthophosphate, polyphosphate and organic phosphorous. Phosphorous in water mostly exists in the form of phosphate which is the essence of soil nutrients and animal and plant bioplasm. Water total phosphorus is examined after all forms of phosphates converted to orthophosphate, and is commonly expressed as milligrams of phosphorus per liter of water (mg/L of P).
Harm of phosphorus in water
In the nitrogen cycle with sufficient oxygen, ammonia nitrogen can be converted into nitrite and nitrate, which may cause cancer in human body. Dissolved ammonia can also be toxic to fish, and discharge of ammonia nitrogen into the water may lead to eutrophication and reduction of the amount of dissolved oxygen. Either case may result in aquatic organisms deaths.
Principle of Molybdovanadate Method
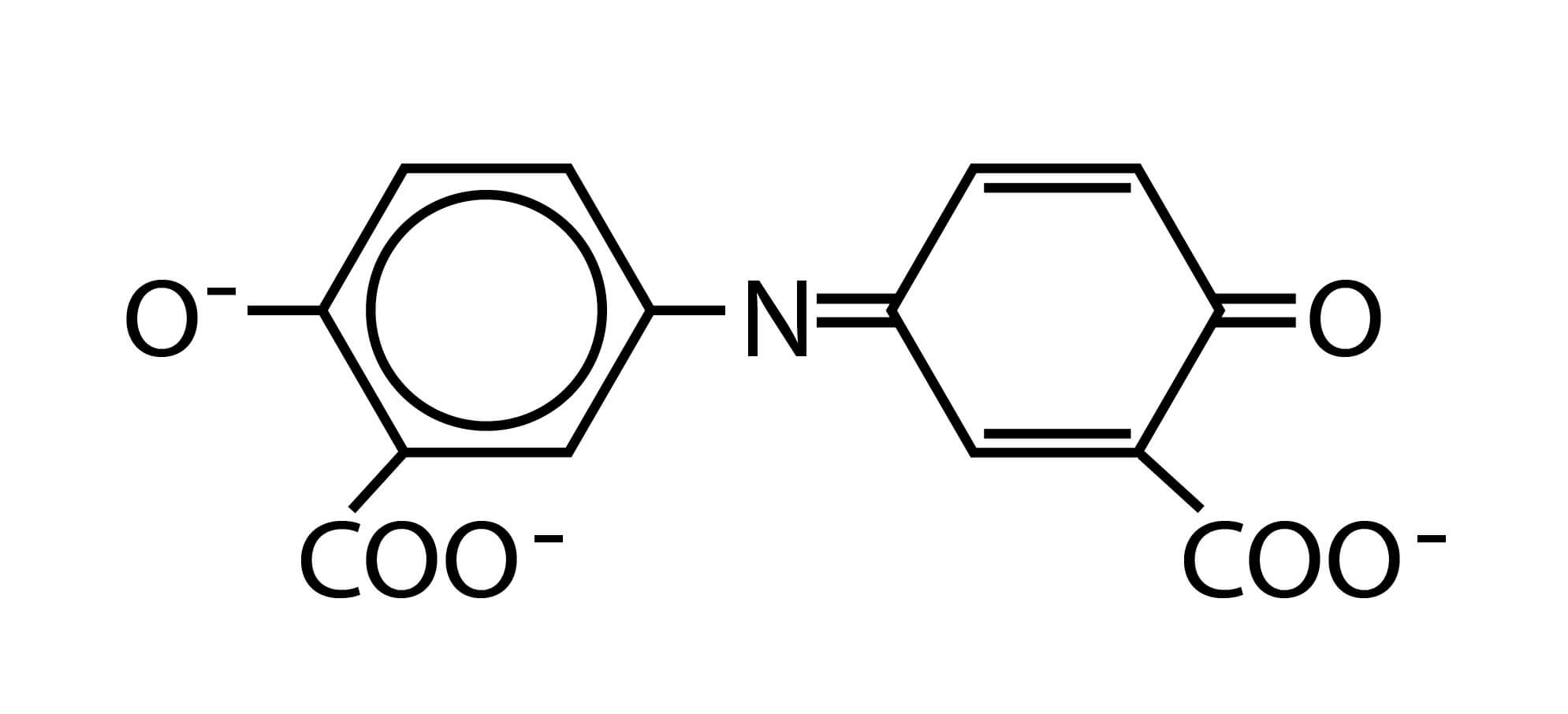
Reactive phosphorus combines with molybdate in an acid medium to form a phosphomolybdate complex. Vanadium, contained in Molybdovanadate Reagent, reacts with the complex to form vanadomolybdophosphoric acid. Intensity of the resulting yellow color is proportional to the concentration of reactive phosphorus.
ROCKER’s COD-test-related products include a reactor, the CR 25, and readers. Compliant with USEPA 410, the CR 25 COD reactor performs closed micro reflux method for metal digestion. The readers, CD 200 and WD 200 are easy to use with their pre-defined programs for COD, Total Phosphorus, Total Nitrogen and Ammonia Nitrogen values.
ROCKER’s Water Analysis Products
WD 100 Water Quality Reader
Determination of Total Nitrogen (TN)
What is Total Nitrogen?
Nitrogen is the sum of various forms of nitrogen in water, including inorganic nitrogen such as nitrate nitrogen (NO3-), nitrite nitrogen (NO2-), ammonia nitrogen (NH4+), and organic nitrogen such as proteins, amino acids, and organic amines. Total nitrogen is an important water quality indicator that reflects water eutrophication. It is usually expressed in milligrams of nitrogen (mg/L N) per liter of water.
Harm of nitrogen in water
Nitrogen is an important element in nature and nutrient of aquatic organisms. However, high content of nitrogen may lead to eutrophication and reduction of the amount of dissolved oxygen and further result in death of fish and aquatic organisms, anoxic water or eutrophication.
Principle of Persulfate Digestion Method
There’re 3 mainstream methods to determine TN (total nitrogen):
- Determine TKN(NH3 + Organic Nitrogen), NO2 and NO3 then make summary of all. (NIEA W423.52C)
- Persulfate Digestion Method
- Gas-Phase Molecular Absorption Spectrometry, GPMAS
An alkaline persulfate digestion converts all forms of nitrogen to nitrate. Sodium metabisulfite is added after the digestion to eliminate halogen oxide interferences. Nitrate then reacts with chromotropic acid under strongly acidic conditions to form a yellow complex. The measur
References:
- Water and Wastewater News | WWD (wwdmag.com)
- Environmental Protection Administration, ROC
- LIN, Kunning, et al. Determination of ammonia nitrogen in natural waters: Recent advances and applications. Trends in Environmental Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 24: e00073.
- HACH, Nitrogen, Ammonia, Method 10023
- HACH, Nitrogen, Ammonia, Method 10031
- HACH, Phosphorus, Total, Method 8190
- HACH, Total Nitrogen, Method 10072