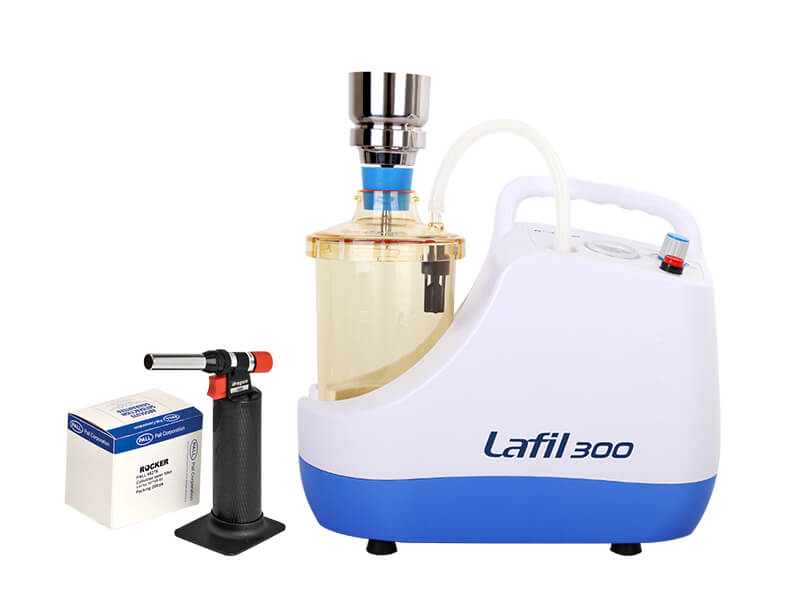
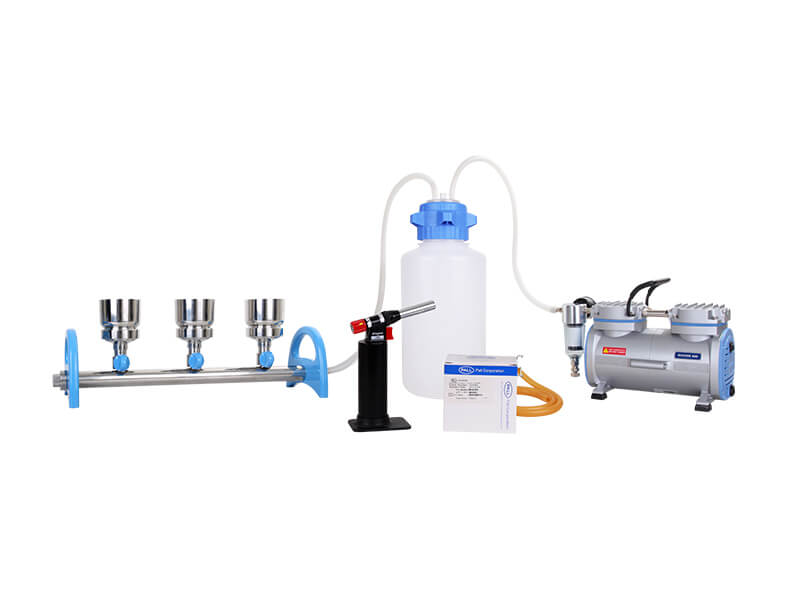
Microbiology test is a vital component of scientific research, clinical diagnostics, and public health. Microbiological testing focuses on the study of microorganisms such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites, and their impact on human health and the environment.
Understanding the importance of microbiology testing is essential as it enables the identification, characterization, and monitoring of microbiological, allowing for the diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases, the detection of microbiological food testing, and the assessment of water and air quality.
By discussing microbiology testing, we delve into the methodologies, advancements, and applications.
What is microbiology test?
Common microbiology testing methods
Microbiology test procedures
Selecting microbial testing equipment
What is microbiology test?
Microorganisms are ubiquitous in the natural environment, and they have been widely used in food manufacturing, such as cheese, beer, bread, and nutritional supplements.
However, certain microorganisms are pathogens, such as E. coli, Salmonella, and Staphylococcus aureus, which can cause discomfort and even fetal harm to the human body. Therefore, microbiology testing and microbial detection are essential for quality control in pharmaceutical manufacturing, food and beverage, and cosmetics industries to ensure product safety.
Common microbiology testing methods
The common methods used for microbiology testing analysis include the multiple-tube fermentation (MPN) method, spread plate method, pour plate method, and membrane filtration method. The membrane filtration method is widely used for the separation of coliform from liquids and has been acknowledged by the U.S. EPA since 1961.
Compared to other methods, the membrane filtration method requires less preparation and provides lower false results and more accurate outcomes. It is considered the primary technology for microorganism separation.
Comparison of different microbial test methods
|
|
Membrane Filtration |
Multiple-tube Fermentation |
Spread Plate |
Pour Plate |
|
Preparation |
Agar plate |
Nutrient broth |
Agar plate |
Agar broth (maintained at between 45~50oC) |
|
Incubation |
24 ± 2 hour |
3 phases, 48 hours/phase |
48 ± 3 hours |
48 ± 3 hours |
|
Consumption |
Membrane, petri dish |
Vials and fermentation tubes |
Petri dish, inoculation hoop |
Petri dish |
|
Sample volume |
High |
Low |
Low |
Low |
|
Heat-sensitive-bacteria-safe |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Sample selection |
Aqueous sample with low turbidity |
Aqueous sample |
Aqueous sample with high bacteria concentration |
Aqueous sample with low bacteria concentration |
|
Accuracy |
High |
Very low |
Low |
Low |
|
Determination |
Observation and counting |
Estimation by MPN |
Observation and counting |
Observation and counting |
|
Colony splitting |
Yes |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Other |
• Membranes can be moved to different culture medium for incubation. • Biocide can be effectively removed. |
• Able to test aqueous samples with high turbidity • Creates more wastes. |
• Culture medium can be easily scratched by the hoop. • Incubation can be processed after dried. |
• Colonies may exist within the culture medium, more difficult to read. |
Microbiology test procedures
Procedure of membrane filter method (NIEA E230.55B):
- The test should be carried out in a laminar flow hood.
- Preparation: Sterilize the stainless steel filtration funnel and tweezers with flame and wait till cool-down.
Rocker’s Bunsen burners provide stable flame up to 1300℃, are the best choice for microbiological food testing!
– Dragon 100 Torch
– Dragon 200 Bunsen Burner
– Dragon 220 Bunsen Burner (45-degree tilt)
Rocker’s Dragon Bunsen Burners
Test procedure:
- Place the sterile membrane filter on the filter holder and dilute it with a few drops of diluent to test if the filtration equipment is properly settled.
- Shake the samples more than 25 times to homogenize them before dilution and detection.
- Filter 100 mL of the samples and then rinse the funnel with 20 mL of diluent.
- Place the membrane onto a petri dish with the appropriate culture medium. Ensure that the membrane is firmly attached to the medium, avoiding any air entering in between.
- Invert the petri dish and place it in the incubator, incubating at 35 ± 1 oC for 24 ± 2 hours. Use a colony counter to count the number of targeted colonies. Note “TNTC” (Too numerous to count) if there are too many colonies.
- Determination: Calculate the bacterial density using the formula noted below: (Colony forming units/100 mL)
CFU formula(CFU equation):

Selecting microbial testing equipment
Microbiology testing, particularly with membrane filtration, often requires sample replication, liquid dispensing, and generates a large amount of liquid waste. Proper waste handling, accurate sample preparation, and equipment sterilization are essential but can be tedious. Here, we share some key points for you to consider when deciding on equipment to simplify your lab life.
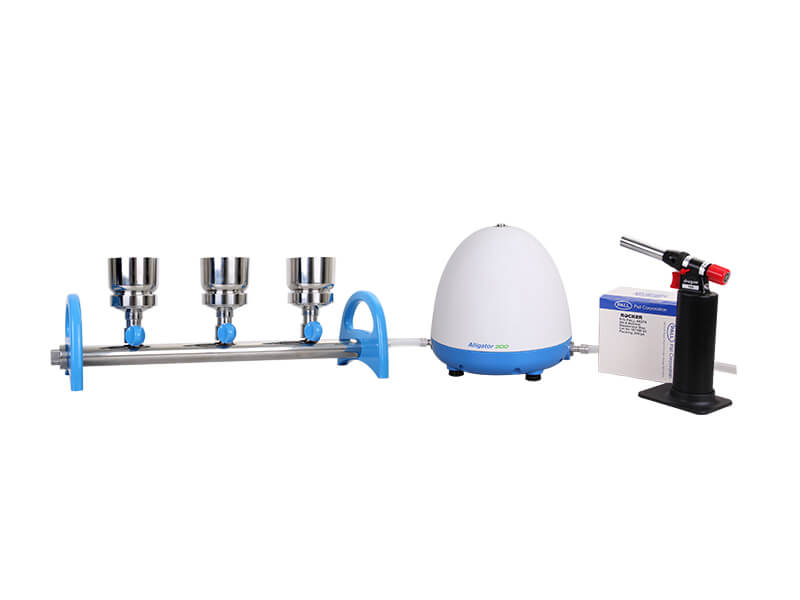
1) Choose equipment that can be sterilized rapidly.
Microbiology testing equipment often requires sterilization using an autoclave, which can take hours to complete. To expedite the process and ensure smoother workflow, consider preparing several sets of equipment for replacement. Alternatively, you can opt for materials that can be rapidly sterilized, such as stainless steel, which can be flame sanitized and ready for use once it has cooled down. This approach saves significant time and facilitates a smoother work procedure, particularly when dealing with a large number of samples to test.
Rocker SF Stainless Steel Filter Holder
– Spin-lock design, no clamps required.
– SS316 – made safe & heat resistant
– Cost-effective, saves up to 46% of long-term budget.
– Eco-friendly, no plastics.
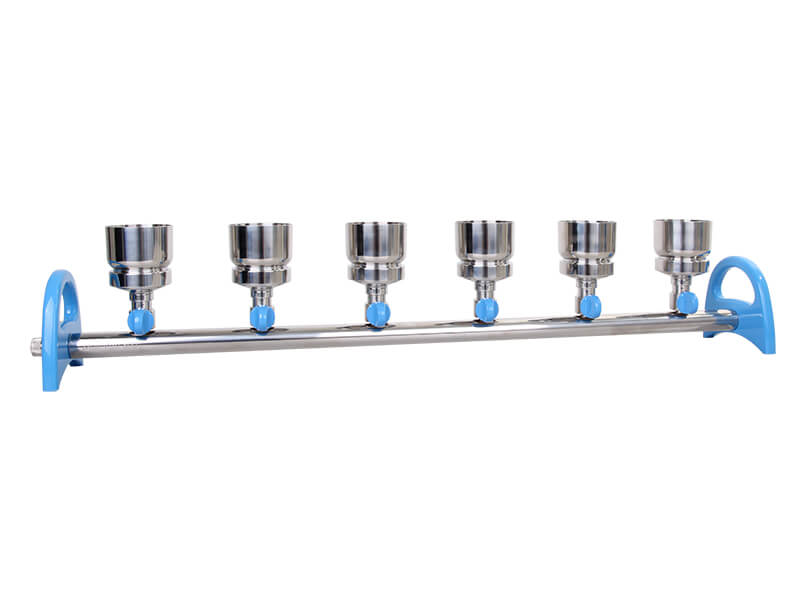
Rocker Stainless Steel Manifold
Rocker Vacuum Manifol Systems
Stainless Manifold and Filter Holders
2) Easier liquid draining
Liquid waste generated from microbiology tests of water samples does not require additional treatment before being drained into the sink. Therefore, there is no need for liquid collection before draining it. Choosing equipment that can directly drain the liquid waste into the sink can save you both effort and time.
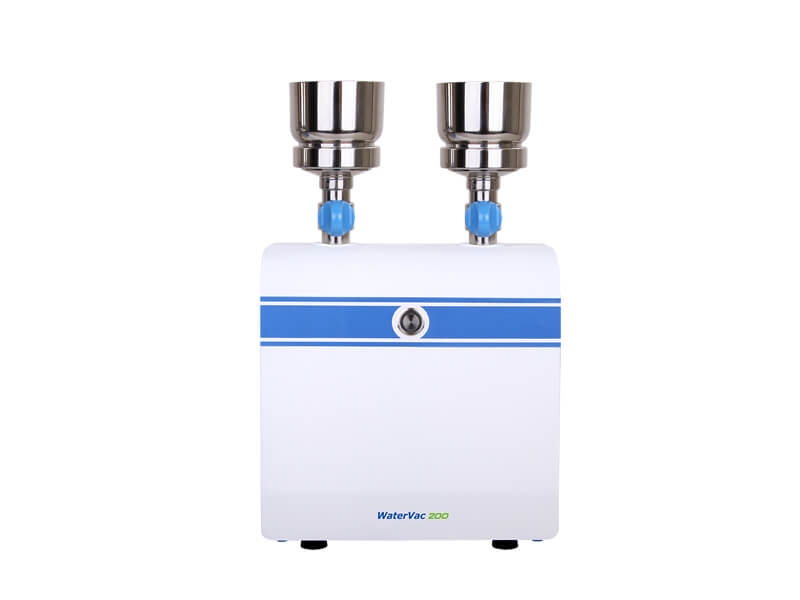
Rocker WaterVac Filtration System
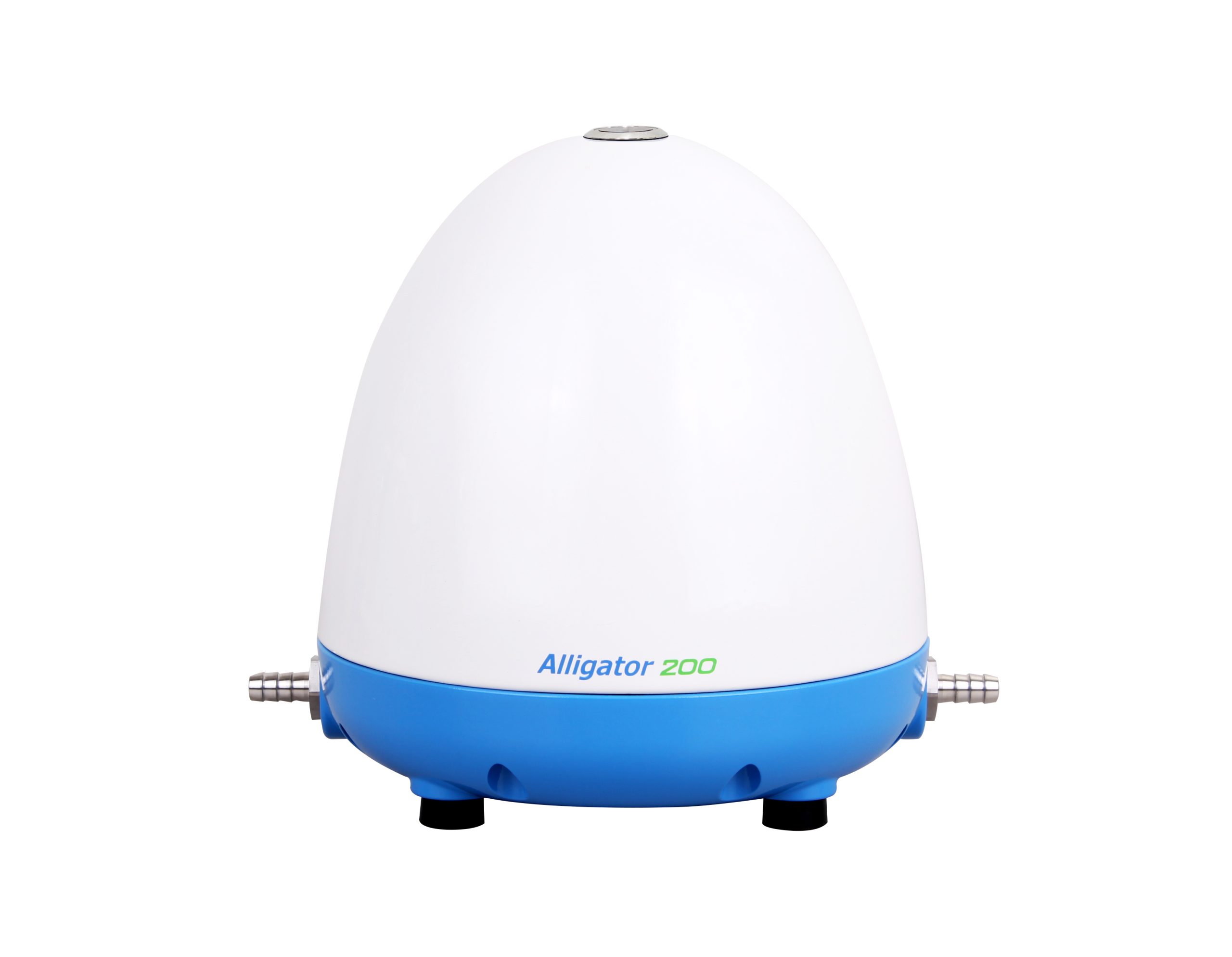
– Alligator 200: Taiwan Excellence award-winning pump
– WaterVac 100: 24VDC-driven, easily portable for at-scene sample collection.
– WaterVac 200: 2 samples at once. Space-saver.
Rocker WaterVac 200 Direct Drain Filtration System
3) Improve sample dispensing efficiency and consistency
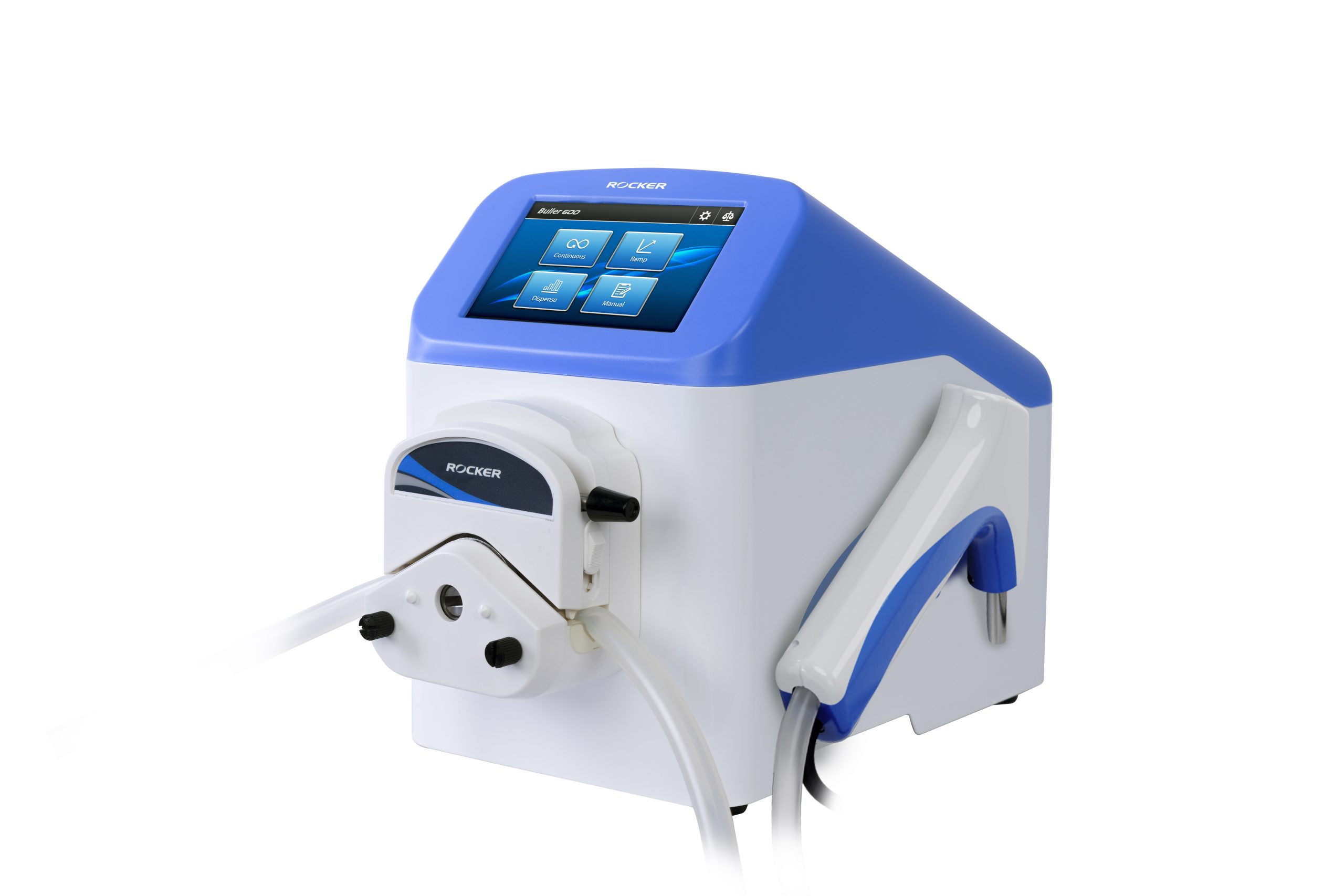
When handling a large number of samples, efficient and precise liquid dispensing becomes critical. We recommend using a dispensing system like the Buller 600 – DSP, which features preset volume settings (such as 2.5 mL, 5 mL, and 9 mL) and an ergonomic handling dispenser. This design not only streamlines operation but also helps maintain dispensing accuracy and consistency, making it particularly suitable for standardized microbiological testing workflows.
Buller 600 – DSP Dispensing Peristaltic Pump
– Design for microbiological test
– Ergonomic & comfortable
– Accurate dispensing
Buller 600 – DSP Dispensing Peristaltic Pump
References:
–Difference Between Pour Plate and Spread Plate
–EQUIVALENT TESTING METHODOLOGY FOR AGRICULTURAL WATER, FDA