Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) is a crucial technique used in analytical chemistry and sample preparation to isolate, concentrate, and purify target compounds from complex matrices. This topic holds significant importance due to its wide range of applications in various fields, including environmental analysis, pharmaceutical research, and forensic science. SPE allows for the selective extraction of analytes based on their affinity for specific solid sorbents, enabling the removal of interfering substances and the enrichment of desired compounds.
By discussing SPE, we gain insights into its principles, methodologies, and advancements, which contribute to improved sensitivity, accuracy, and efficiency in analytical workflows. Therefore, exploring the topic of solid phase extraction is essential for researchers and analysts seeking reliable and efficient methods for sample purification and analysis.
What is Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)?
Advantage of SPE compared to LLE and SLE
Solid Phase Extraction Steps
Solid Phase Extraction Applications
Solid Phase Extraction Equipment
What is Solid Phase Extraction (SPE)?
Solid phase extraction (SPE) is a common sample pre-treatment technique. It has been developed from solid-liquid extraction and chromatography methods and is often used for sample fractionation, purification, enrichment, and concentration.
Similar to liquid chromatography (LC), in the SPE process, interfering components are separated from analytes due to differences in affinity and adsorption.
SPE is one of the most common sample pre-treatment techniques used before HPLC, LC, and GC-MS analysis due to its ease of operation, ability to simplify analysis, and increase sensitivity. The major advantages of using SPE include:
-
Make the sample simpler and cleaner. Samples often have a complex composition. Interferents can reduce sensitivity and also shorten the lifespan of columns and instruments. SPE treatment can provide clean extraction of analytes and yield more accurate results.
-
Concentration and trace enrichment. SPE is advantageous when researchers aim for low detection levels, such as parts per billion (ppb, 10-9) or parts per trillion (ppt, 10-12), as the SPE process facilitates sample enrichment and purification with ease.
-
Compound fractionation. SPE can effectively separate multiple compounds from samples based on specific characteristics, such as polarity or non-polarity.
Advantage of SPE compared to LLE and SLE
Statistically, sample preparation and pre-treatment account for 80% of the time and costs involved in modern scientific analysis. Adopting simpler and faster pre-treatment methodologies can provide significant benefits for all scientists.
In addition to SPE, there are several other commonly used sample pre-treatment methods, such as Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE), Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE), and Protein Precipitation (PPT).
|
|
Solid Phase Extraction (SPE) |
Liquid-Liquid Extraction (LLE) |
Supported Liquid Extraction (SLE) |
|
Method development |
Required |
Required |
Required |
|
Pollution factors |
Less solvent and plastic wastes |
A lot solvent wastes |
Some solvent and plastic wastes |
|
Operational safety |
Safe (exposure to solvent) |
No safe (exposure to solvent, potential to explosion) |
Safe (exposure to solvent) |
|
Main costs |
Extraction Column |
Solvent, powdered solvent |
Extraction Column |
|
Sample requirement |
Less |
More |
Middle |
|
Emulsion |
None |
Yes |
None |
|
Sensitivity |
High |
Low |
Middle |
|
Heating concentration |
Not required |
Required |
Not required |
|
Automation |
Possible |
Not possible |
Possible |
|
Speed |
Middle |
Slow |
Fast |
|
High throughput |
High |
Middle |
High |
|
Limitation |
None |
Not suitable for very polar analytes |
None |
Solid Phase Extraction Steps
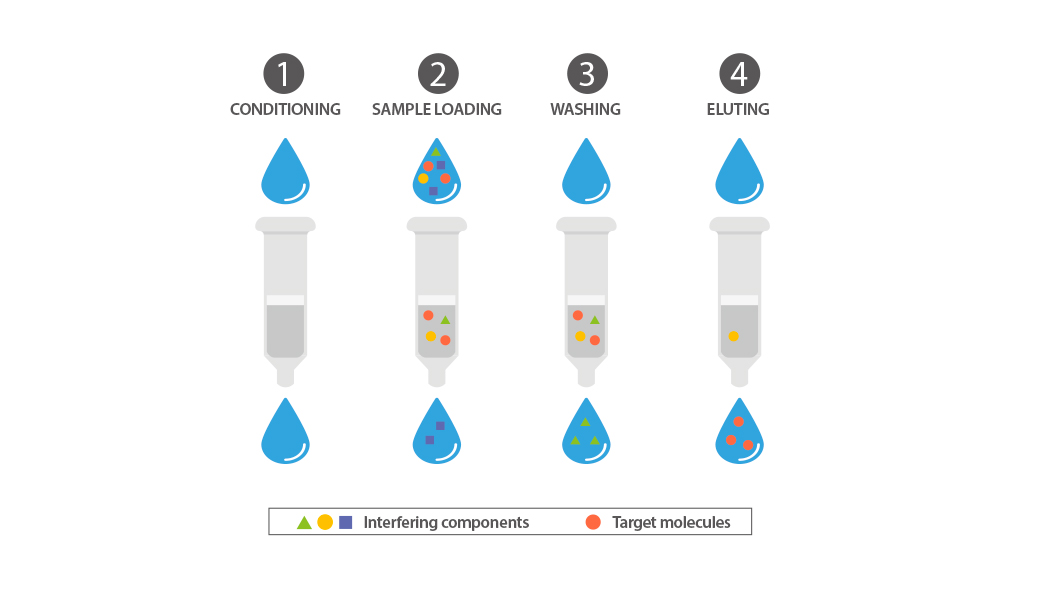
There are four major steps in the solid phase extraction process:
-
Conditioning: This involves priming the cartridge to prepare it for accepting the target analyte.
-
Sample loading: The sample is loaded onto the cartridge at a suitable flow rate, allowing the target analytes to be adsorbed or collected by the adsorbent.
-
Washing: The cartridge is rinsed with a solvent or 100% H2O to remove interferents that were not retained by the adsorbent. Additional rinses can be performed using solvents of increasing polarity (e.g., 5%, 10%, 20%, 100%) to remove compounds based on decreasing polarity.
-
Elution: This step involves releasing the analytes from the adsorbent, typically using an elution solvent or a combination of solvents.
Solid Phase Extraction Applications
-
- Pharmaceutical industry, such as components extraction and research of metabolite.
- Environmental Analysis, such as extraction of metals in water.
- Food testing, such as pesticide and veterinary drug residues.
- Switch sample matrices to be more compatible with the target chromatographic method.
- Concentrate analytes (trace enrichment) for increased sensitivity.
- Remove interferences that cause high background, misleading peaks, and/or poor sensitivity during chromatographic analysis.
- Protect the analytical column from contaminants. Automate the extraction process.
Solid Phase Extraction Equipment
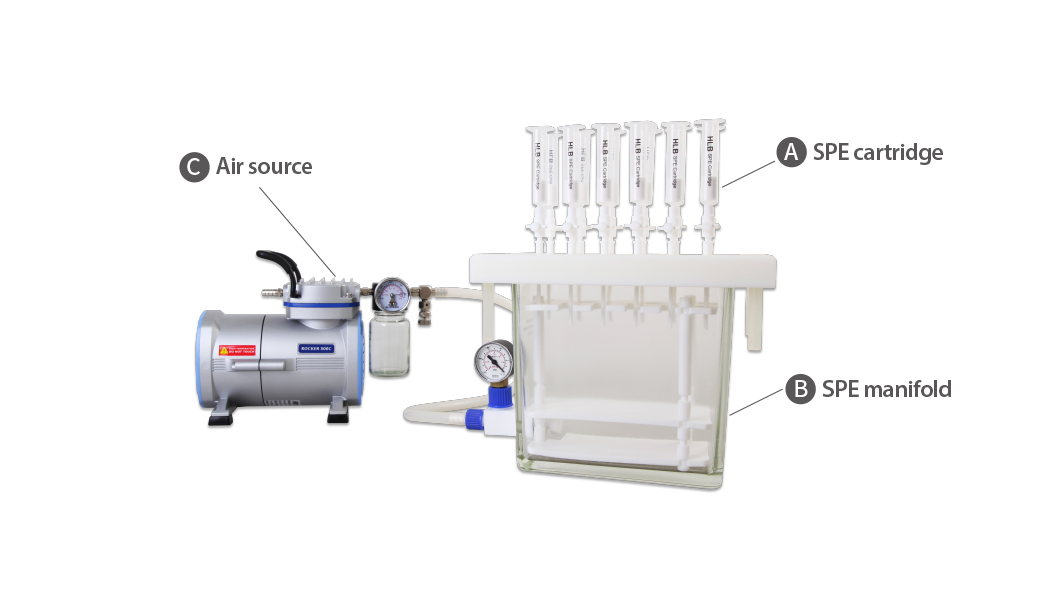

The most common type of SPE is adsorption, which involves using an SPE cartridge(SPE column) containing adsorbents installed on a filter device. Air pressure devices can be used to expedite the exchange process.
A. SPE cartridge / SPE column
There are various types available, including columns, membranes, 96-well microplates, or pipette tips filled with adsorbents.
B. SPE manifold
This device is used to hold and support the cartridges or membranes during the SPE process.
 |
 |
|
SPE Manifold (Column type) |
SPE Manifold (Membrane type) |
C. Other device
The most commonly used devices in the SPE process are air compressors or vacuum pumps, which help accelerate the flow of liquids. However, a high-speed flow may result in a lower reaction efficiency. Therefore, it is advisable to use a pump or compressor with a regulator to control the flow rate. Additionally, since the SPE process often involves solvents such as methanol or acetonitrile, it is highly recommended to use devices that have chemical resistance to ensure device lifespan and safety during operation.
References:
- WatersTM Beginner’s Guide to SPE
- Mass Spectrometry for the Clinical Laboratory, 2017, Pages 37-62
- Comprehensive Sampling and Sample Preparation, 2012
- Solid Phase Extraction Guide, Thermo Fisher