What’s a cleanliness test?
Why parts do cleanliness tests?
Common fields that apply cleanliness testing
Cleanliness testing methods
Choosing proper solvents for cleanliness testing
Common types of contamination of cleanliness testing
What’s a cleanliness test?
Cleanliness (cleanliness) refers to the degree to which specific parts of parts, assemblies, and complete machines are polluted by impurities, and indicates the amount of pollutants remaining on the surface of parts or products after cleaning. Characteristic parameters such as the quality, size and quantity of the impurity particles collected at specific parts are expressed.
The cleaning of components and parts is very important for mass production and quality control of finished products, especially in the automotive, aerospace, semiconductor and other industries. Because the manufacturing process, transportation, and environment may produce pollution, such as fine particles, non-volatile residues (NVR), etc., these surface pollution will have a direct impact on product function, reliability, and even service life. Each has corresponding standards for cleanliness, such as ISO 16232 and VDA 19.1 for the automotive industry.
Why parts do cleanliness tests?
The cleanliness of parts (cleanliness) is closely related to the service life of products. Contaminants can cause corrosion, wear, short circuit, signal distortion and abnormal signal on the surface of parts and components. When using the product, it may cause product function failure, poor operation, noise, etc. to shorten the service life of the product. In severe cases, it may even cause harm and dangerous safety problems when the product is used. The cleanliness (cleanliness) measurement method is very important for process control, quality assurance, and failure analysis. It is a detailed process for obtaining data on the cleanliness (cleanliness) of measurement subjects such as various mechanical equipment and electronic parts.
If the product is contaminated, it will directly affect the reliability and service life of the finished product. Dangers to products posed by unclean surfaces or process fluids include functional failure, product failure, and even complete product failure. Dirt residues on the surfaces of technical equipment used in the manufacturing and assembly process can lead to unreliable or poor equipment performance and even cause production downtime, wasted material and energy issues. Larger residual particles (sometimes referred to as “particle killers”) can completely disable a product’s functionality. As system components continue to shrink in size, even smaller residual particles can cause catastrophic failure and scrap the entire finished product. Many of today’s high-tech industries require cleanliness inspections. Industries with precision processes and trace pollution are likely to cause defective products, regardless of the raw materials at the beginning, the production environment, the equipment, personnel used, and the final packaging materials. Transportation requires strict control over cleanliness (cleanliness).
Common fields that apply cleanliness testing
- Photoelectric & semiconductor
- Automation equipment
- Precision machinery
- Medical equipment
- Automotive industry
- Printed circuit board
- Hard drive components
- Clean room supplies
Cleanliness testing methods
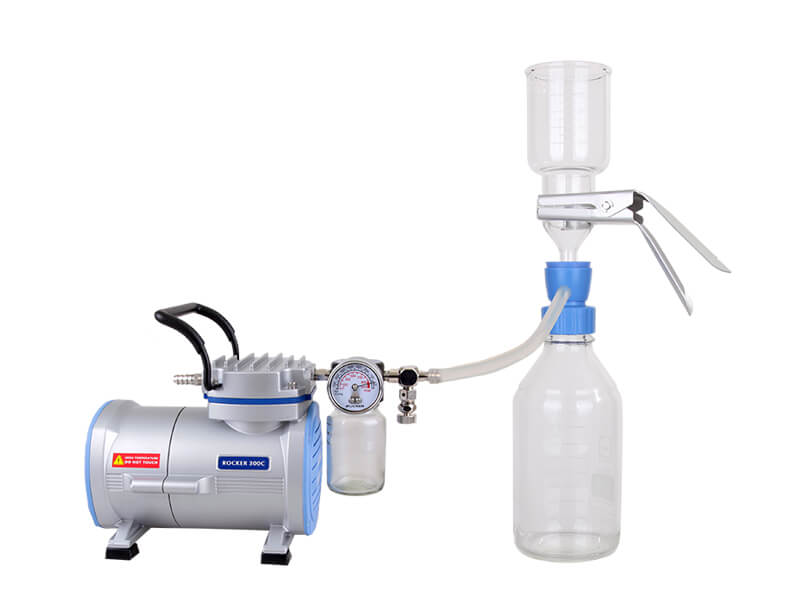
The cleanliness test is to use stirring, pressure, ultrasonic washing and other methods to clean the contaminated particles on the surface of the parts, filter the cleaning solution and collect the contaminated particles, and finally analyze the size, weight, quantity, shape and other indicators according to the product characteristics and cleanliness requirements .
The purpose of the cleanliness test is to avoid problems such as shortened product life and reduced reliability by monitoring the amount of residual contamination on the surface of parts and products. The steps are: cleaning/extracting → filtering → drying → weighing→ checking and analyzing →microscopic inspection → result
Clean a certain number of parts under certain conditions, fully filter the filter membrane through which the cleaning solution passes, and collect the dirt on the surface of the filter membrane, then dry the filter membrane, and detect it under light irradiation with a microscope, according to the particles The size and number of dirt particles can be counted to obtain the solid particle pollution results of the measured object parts.
The choice of cleaning solution is usually an aqueous neutral cleaning solution containing a surfactant, a non-polar solution (such as dichloroethane) or a polar solution (such as ethanol), so it is recommended to assist with a corrosion-resistant vacuum pump to speed up the overall filtration speed, and at the same time slow down the erosion of chemical substances on the pump.
Stirring method
Block the opening of the test sample, partially or completely fill it with cleaning solution, then shake or stir to extract the particles from the designated area, shake the sample vigorously in all directions to make the cleaning solution fill all hollow areas, Parameters can be adjusted and set according to sample shape, size and weight. For example, for a brake fluid tank, the stirring parameters that can be used are frequency of 100~200 times per minute, amplitude of 50~150mm, shaking for 5~15 seconds.
It is suitable for the detection of particle content in hollow parts or products, manual or mechanical automatic stirring, but not suitable for the determination of particle content in liquid or gas samples. Influencing factors includes whether the stirring method is manual or automatic, amplitude, frequency, stirring time, type and amount of cleaning solution.
Pressure flushing method
Depending on the shape of the sample and the area to be cleaned, different sizes and shapes of nozzles or guns should be used.
Pressure washing is suitable for external areas that are directly accessible and can be cleaned with ring nozzles for large surfaces, internal cavities or hard-to-reach external areas cannot be cleaned with nozzles, but short boreholes with large diameters can still use the direct spray method; when Where direct contact of such geometries is not possible with a pressure washer jet, a pressure washer gun should be used to penetrate deeper into internal cavities, or a small diameter drilled hole should be selected.
Influencing factors include: flushing pressure, liquid flow rate, flushing distance and angle, nozzle size and shape (flat or round), cleaning sequence, sample processing, cleaning time, liquid consumption per unit area, etc.
Ultrasound
Bath or ultrasonic cleaner for cleaning. It is suitable for small or medium-sized parts with simple external shape and internal and external cleaning, such as gears and joint sealants, but not suitable for cleaning liquid or gas materials, gray cast iron, and cast aluminum parts. Influencing factors include ultrasonic density, time, medium, the relative relationship between the position and orientation of the sample and the ultrasonic source, and the material of the sample.
Choosing proper solvents for cleanliness testing
The main function of the cleaning fluid is to remove the adhesion or layer between the particle and the surface, effectively separating the contamination without affecting the liquid on the surface of the part. When selecting, attention should be paid to its compatibility with the sample material, liquid in the system, test equipment, filter paper, and filtration system. Low flow rate, viscosity ≤ 5mm2/s, can remove or dissolve grease, and it needs to be filtered in advance for extraction. , you should also pay attention when choosing:
- Verify the suitability of aqueous neutral cleaners containing surfactants (such as deionized water).
These are typically used in aqueous coolant/lubricant emulsions, animal and vegetable fats and oils, and amino-based preservatives (ensure no foam). - If not available, check the suitability of the non-polar solutions mentioned above (dichloroethane, etc.).
These are especially suitable for removing mineral oil-based lubricants or preservatives. - If the above two sets of solutions are not suitable, you must choose a special cleaning liquid, such as alcohol (ethanol, polar solution) to remove the brake fluid.
When making this selection, ensure that the cleaning agent is compatible with the component material. Especially when hydrocarbons are used, incompatibility between the plastic and the surface of the coating may occur. Aqueous neutral cleaners containing surfactants should not be used with magnesium or magnesium alloys.
Common types of contamination of cleanliness testing
-
- Particulate/Particulate Contamination
Particulate contamination of varying sizes can cause equipment to wear out, fail, clog, malfunction, and lose control. - Corrosive chemical contamination
Corrosion of metal parts and products, corrosive fogging of optical components, short circuits of electronic circuits. - Precipitation chemical substance pollution
Interference with telecommunication strength, signal distortion and signal abnormality, abnormal circuit impedance, product overheating, adhesive failure, optical component adhesive fogging.
- Particulate/Particulate Contamination
Reference: SGS TAIWAN